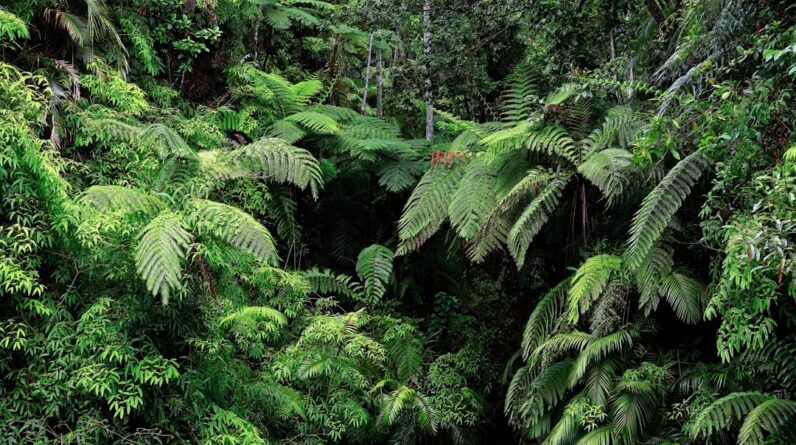
Reforestation plays a crucial role in wildlife conservation, serving as a vital strategy to restore ecosystems that have been degraded or destroyed. When you think about the myriad of species that depend on forests for their survival, it becomes clear that reforestation is not just about planting trees; it’s about creating habitats that support biodiversity. Forests provide food, shelter, and breeding grounds for countless animals, from the smallest insects to large mammals.
By reintroducing trees into barren landscapes, you are essentially reviving entire ecosystems, allowing wildlife populations to thrive once more. Moreover, reforestation helps combat climate change, which is one of the most pressing threats to wildlife today. Trees absorb carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming.
By increasing forest cover, you are not only providing a home for wildlife but also mitigating the effects of climate change that can lead to habitat loss. This dual benefit underscores the importance of reforestation in wildlife conservation efforts. As you engage in or support reforestation initiatives, you are contributing to a healthier planet and ensuring that future generations of wildlife can flourish.
Key Takeaways
- Reforestation is crucial for wildlife conservation as it provides habitat and food sources for a variety of species.
- Selecting the right tree species is essential for creating a suitable wildlife habitat during reforestation projects.
- A successful reforestation plan involves careful consideration of factors such as soil type, climate, and the needs of local wildlife.
- Community involvement is key to the success of reforestation projects, as it fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility for the restored areas.
- Monitoring and maintaining reforested areas is important for ensuring that they continue to provide valuable habitat for wildlife.
Selecting the Right Tree Species for Wildlife Habitat
Choosing the appropriate tree species is fundamental to the success of any reforestation project aimed at enhancing wildlife habitats. You must consider the specific needs of the local fauna when selecting trees. Native species are often the best choice because they have co-evolved with local wildlife and provide the necessary food and shelter that these animals require.
For instance, certain birds may rely on specific trees for nesting, while various insects may depend on particular plants for sustenance. By prioritizing native species, you ensure that the reforested area will support a diverse range of wildlife. In addition to native species, it’s essential to consider the ecological characteristics of the area where you plan to reforest.
Factors such as soil type, climate, and existing flora will influence which tree species will thrive. You might find that some areas are better suited for fast-growing species that can quickly provide cover and food, while others may benefit from slower-growing trees that offer long-term stability and habitat complexity. By carefully selecting tree species based on these criteria, you can create a more resilient and biodiverse ecosystem that supports a wide array of wildlife.
Establishing a Successful Reforestation Plan
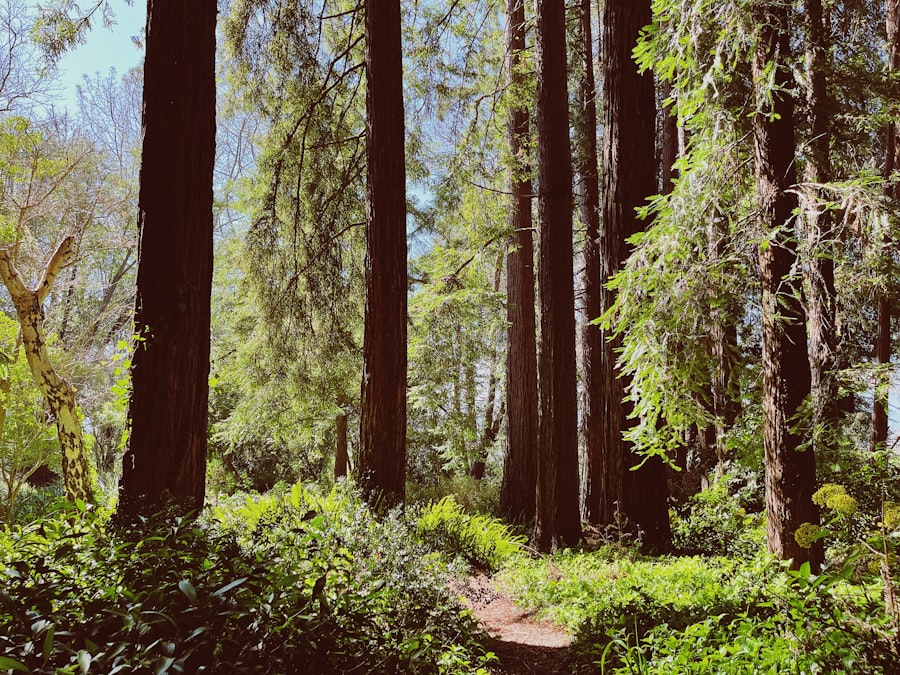

Creating a successful reforestation plan requires careful planning and execution. You need to start by assessing the land you wish to reforest. This involves understanding the current state of the ecosystem, identifying any invasive species that may need to be removed, and determining the best approach for planting new trees.
A thorough site assessment will help you understand the challenges you may face and allow you to develop strategies to overcome them. This groundwork is essential for ensuring that your reforestation efforts will be effective in restoring wildlife habitats. Once you have a clear understanding of the site, you can begin to outline your reforestation goals.
Are you aiming to restore a specific habitat type? Do you want to increase biodiversity or improve carbon sequestration? Setting clear objectives will guide your actions and help you measure success over time.
Additionally, consider involving local stakeholders in your planning process. Engaging with community members, conservation organizations, and local governments can provide valuable insights and foster a sense of ownership over the project. This collaborative approach not only enhances the likelihood of success but also builds a network of support for ongoing conservation efforts.
The Role of Community Involvement in Reforestation Projects
Community involvement is a cornerstone of successful reforestation projects. When local people are engaged in the process, they are more likely to take ownership of the project and ensure its sustainability over time. You can encourage community participation by organizing workshops and educational programs that highlight the importance of reforestation for both wildlife conservation and local livelihoods.
By fostering a sense of connection between community members and their natural environment, you empower them to become stewards of their local ecosystems. Moreover, involving the community can lead to innovative solutions tailored to local needs and conditions. Residents often have valuable knowledge about their environment and can provide insights into which tree species would thrive in specific areas or how best to manage invasive species.
By tapping into this local expertise, you can enhance the effectiveness of your reforestation efforts while also building trust and collaboration among stakeholders. Ultimately, community involvement not only enriches the reforestation process but also strengthens social ties and promotes a culture of conservation.
Monitoring and Maintaining Reforested Areas for Wildlife
Once your reforestation project is underway, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure its success. You need to establish a system for tracking the growth and health of newly planted trees as well as the wildlife that begins to return to these areas. Regular assessments will help you identify any issues early on, such as pest infestations or diseases that could threaten both the trees and the wildlife they support.
By staying vigilant, you can take proactive measures to address these challenges before they escalate. In addition to monitoring tree health, it’s important to observe how wildlife is responding to the reforested area. Are animals returning?
Are they utilizing the habitat as expected? Gathering data on wildlife populations can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of your reforestation efforts. This information can also inform future projects and help refine your strategies for enhancing wildlife habitats.
Maintenance activities such as thinning overcrowded areas or planting additional species may be necessary as the ecosystem evolves over time. By committing to ongoing care and observation, you ensure that your reforested areas continue to thrive as vibrant habitats for wildlife.
Creating Wildlife Corridors through Reforestation
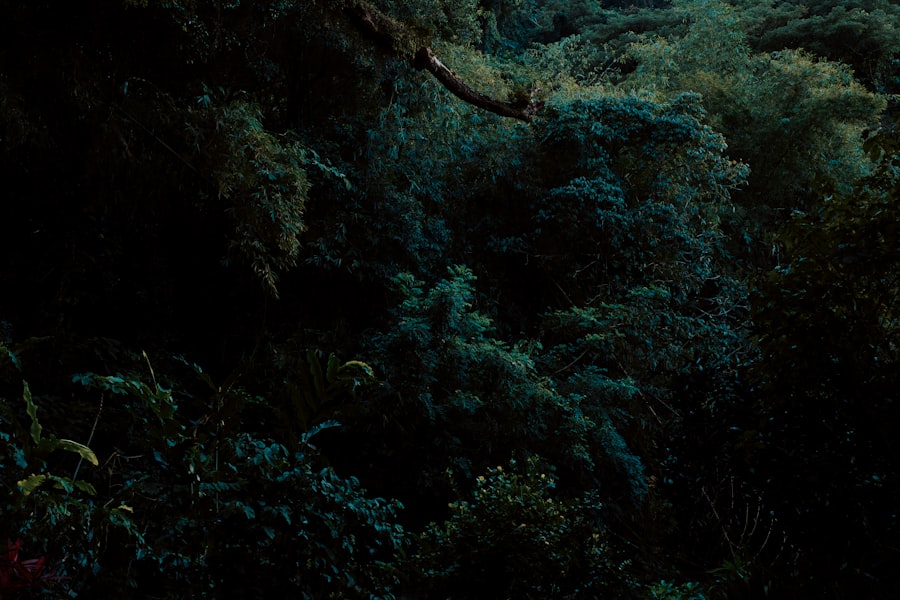

Wildlife corridors are essential for maintaining biodiversity and facilitating animal movement between fragmented habitats. As you engage in reforestation efforts, consider how your projects can contribute to creating these vital corridors. By strategically planting trees in areas that connect existing habitats, you can help mitigate the effects of habitat fragmentation caused by urban development or agriculture.
These corridors allow animals to migrate safely between different areas, promoting genetic diversity and reducing the risk of extinction for isolated populations. When designing wildlife corridors through reforestation, it’s important to consider the specific needs of the species you aim to protect. Different animals have varying requirements for movement; some may prefer open spaces while others need dense cover for safety.
By incorporating a mix of tree species and creating varied habitat structures within your corridors, you can cater to a wider range of wildlife needs. Additionally, engaging with local communities in this planning process can help identify key areas where corridors would be most beneficial, ensuring that your efforts align with both ecological goals and community interests.
Case Studies of Successful Reforestation Projects for Wildlife
Examining successful case studies can provide valuable lessons for your own reforestation efforts aimed at wildlife conservation. One notable example is the restoration of the Atlantic Forest in Brazil, which has been severely impacted by deforestation over the years. Through collaborative efforts involving local communities, NGOs, and government agencies, large-scale reforestation initiatives have been implemented to restore this critical habitat.
These projects not only focus on planting native tree species but also emphasize community engagement and education about sustainable land use practices. Another inspiring case is found in Madagascar, where organizations have worked tirelessly to restore degraded landscapes while protecting unique wildlife species such as lemurs. By integrating agroforestry practices with reforestation efforts, these projects have created sustainable livelihoods for local communities while simultaneously enhancing biodiversity.
The success stories from these regions highlight the importance of collaboration, adaptive management, and community involvement in achieving meaningful outcomes in wildlife conservation through reforestation.
The Future of Reforestation and Wildlife Conservation
As we look toward the future, reforestation will continue to play an integral role in wildlife conservation efforts worldwide. With increasing awareness of environmental issues such as climate change and habitat loss, there is a growing movement toward sustainable land management practices that prioritize ecosystem restoration. You have an opportunity to be part of this movement by supporting or initiating reforestation projects in your area or beyond.
Technological advancements also hold promise for enhancing reforestation efforts. Innovations such as drone technology for seed dispersal or remote sensing for monitoring forest health can improve efficiency and effectiveness in restoration projects. As these tools become more accessible, they will empower individuals and organizations alike to take action in restoring habitats for wildlife.
The future of reforestation is bright, driven by collective action and a shared commitment to preserving our planet’s biodiversity for generations to come.
If you are interested in learning more about the benefits of tree planting beyond creating wildlife havens, check out this article on preventing floods by massive tree planting. It discusses how reforestation efforts can help mitigate the impact of flooding and protect communities from natural disasters. This article provides valuable insights into the multifaceted benefits of planting trees and the positive impact it can have on the environment.
FAQs
What is reforestation?
Reforestation is the process of planting trees in areas where forests have been depleted or destroyed. It aims to restore the ecological balance and increase the biodiversity of an area.
Why is reforestation important for wildlife?
Reforestation is important for wildlife because it provides habitat and food sources for a wide variety of species. It also helps to create corridors for wildlife to move through and increases the overall biodiversity of an area.
How does reforestation create wildlife havens?
Reforestation creates wildlife havens by providing new habitats for animals and plants to thrive. As trees and other vegetation grow, they attract a variety of wildlife, creating a diverse and healthy ecosystem.
What are some benefits of reforestation for the environment?
Reforestation helps to combat climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. It also helps to prevent soil erosion, improve water quality, and create a more sustainable environment for future generations.
What are some challenges of reforestation?
Challenges of reforestation include finding suitable land for planting, securing funding for large-scale projects, and ensuring the long-term survival of newly planted trees. Additionally, invasive species and climate change can pose challenges to the success of reforestation efforts.